What is a Root SSL Certificate?
A Root SSL certificate is a certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA).
In the SSL ecosystem, anyone can generate a signing key and use it to sign a new certificate. However, that certificate isn’t considered valid unless it has been directly or indirectly signed by a trusted CA.
A trusted certificate authority is an entity that’s entitled to verify someone is who they say they are. In order for this model to work, all participants must agree on a set of trusted CAs. All operating systems and most web browsers ship with a set of trusted CAs.
The SSL ecosystem is based on a model of a trust relationship, also called the “chain of trust”. When a device validates a certificate, it compares the certificate issuer with the list of trusted CAs. If a match isn’t found, the client checks to see if the certificate of the issuing CA was issued by a trusted CA, and continues until the end of the certificate chain. The top of the chain, the root certificate, must be issued by a trusted Certificate Authority.
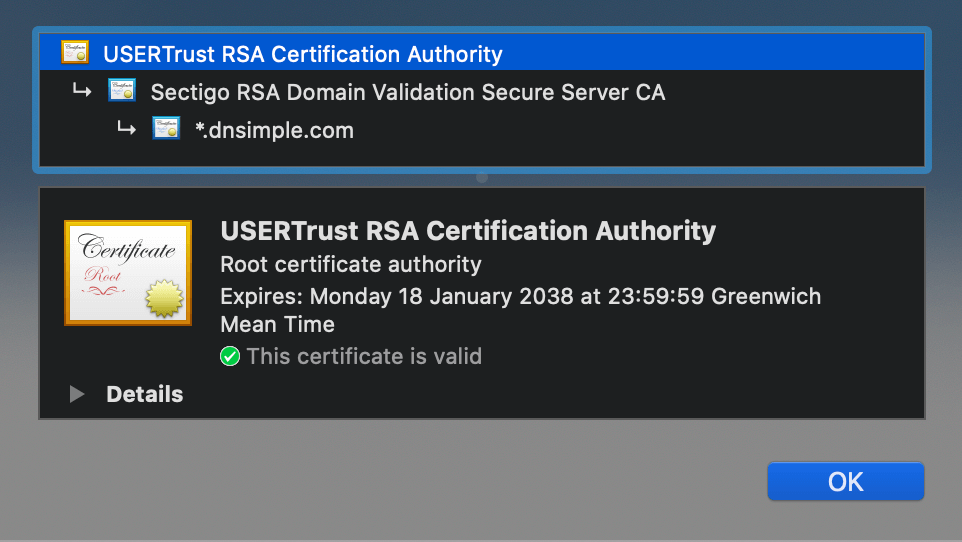
The list of trusted CAs is critical, because it determines the security level of an entire system.